Article
Malygin V.L., Merkurieva Yu.A., Shevchenko Yu.S., Malygin Ya.V., Ponomareva M.V. (2018) Psychological features and social adaptation of internet-addicted adolescents and adolescents with cannabinoid addiction. National Psychological Journal. 3, 90-97.
Abstract
The Objective of the research is to study the characteristics of character properties, emotional intelligence, social psychological adaptation of Internet addicted adolescents and adolescents addicted with drugs.
Design. A comparative study of the psychological properties of cannabinoid addicted adolescents (n = 20) and Internet addicted adolescents (n = 20), and also healthy adolescents without symptoms of addiction (n = 20) is conducted. The following methods are used in the study: Barratt’s impulsiveness scale (BIS-11), 1987, adapted by T.I. Medvedeva and S.N. Enikolopov, 2015, Cloninger temperament and character questionnaire (TCI-125), 1991, adapted by N.A. Almaev and L.D. Ostrovskaya, 2005, the methodology for diagnosing emotional intelligence MSCEITV 2.0 2002, adapted by E.A. Sergienko, N.I. Vetrova, 2009, the methodology for diagnosing the social psychological adapted by K. Rogers and R. Diamond, 1954, adapted by A.K. Osnitsky, 2002, Chen Internet Addiction Scale (CIAS), 2003 adapted by V.L. Malygin and K.A. Feklisov, 2010
Results. Adolescents with Internet addiction and adolescents with cannabinoid addiction have a certain similarity in a number of characteristic features. They are characterized by a more pronounced motor impulsiveness, low self-control, low self-esteem, dependence on other individulas and circumstances, lack of clear life goals. In general, if compared to healthy adolescents they appear to be infantile individuals, socially maladjusted, more often experiencing emotional discomfort, which can result in pathologies, i.e. particularly various types of addictive behaviour. Simultaneously, Internet-dependent adolescents are significantly different from those with cannabinoid addiction. They are characterized by a lower level of transcendence and a lesser inclination to spiritual practices and transpersonal experience accordingly. They have a low level of search for novelty, which characterizes them as conservative, rigid and passive individuals.
Conclusion. The data obtained reveal certain differences in the psychological mechanisms of Internet addiction and dependence on drugs. Psychological mechanisms of adolescent Internet addiction and dependence on cannabinoids have significant differences.
Accepted: 09/03/2018
Pages: 90-97
DOI: 10.11621/npj.2018.0308
PDF: Download
Keywords: teenagers; cannabinoid addiction; adolescent Internet addiction; psychological risk factors; psychological mechanisms of addiction;
Available Online 30.09.2018
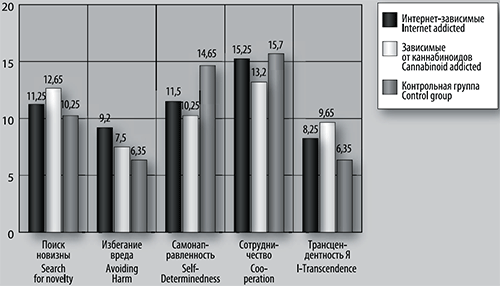
Fig. 1. Results of the Cloninger test Note: statistically significant differences are marked as *
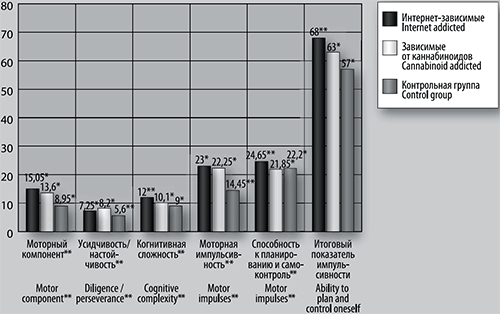
Fig. 2. Results of Barratt’s impulsiveness scale Note: statistically significant differences are indicated as ** in case of differences between the two groups and as * in case of differences in the three groups.
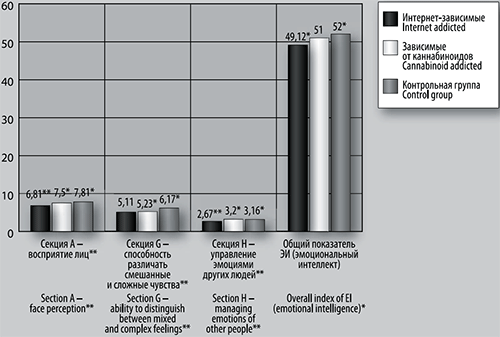
Fig. 3. Results of the emotional intelligence study. Notes: Data are given in raw scores, statistically significant differences are indicated as *
References:
Adams, B. L. M. et al. (2018) Internet Gaming Disorder Behaviours in Emergent Adulthood: a Pilot Study Examining the Interplay Between Anxiety and Family Cohesion. International Journal of Mental Health and Addiction, 1–17.
Bahraminezhad, A. et al. (2017) The relationship between emotional intelligence and addiction tendency in students of Lorestan University of Medical Sciences. Yafte, 19, 4.
Bielefeld, M. et al. (2017) Comorbidity of Internet use disorder and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: Two adult case–control studies. Journal of behavioural addictions, 6(4), 490–504. doi: 10.1556/2006.6.2017.073
Bogacheva, N.V. (2014) Computer games and psychological specifics of the cognitive sphere of gamers. [Vestnik Moskovskogo universiteta]. Series 14. Psychology, 4, 120–130.
Bogacheva, N.V. (2015) Computer games and the psychological specifics of the cognitive sphere of gamers (ending) [Vestnik Moskovskogo universiteta]. Series 14. Psychology, 1, 94–103.
Bukhanovsky, A.O. (2002) Dependent behaviour: clinic, dynamics, categorisation, treatment, prevention. Rostov-on-Don, Feniks, 360.
Cimino, S., & Cerniglia, L. (2018) Research Article. A Longitudinal Study for the Empirical Validation of an Etiopathogenetic Model of Internet Addiction in Adolescence Based on Early Emotion Regulation.
Crippa, J.A., Zuardi, A.W., & Martin Santos, R et al. (2009) Cannabis and anxiety: a critical review of the evidence. Hum Psychopharmacol, 24(7), 515–523. doi: 10.1002/hup.1048
Degenhardt, L, Hall, W, & Lynskey, M. (2001) The relationship between cannabis use, depression and anxiety among Australian adults: findings from the National Survey of Mental Health and Well Being. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol, 36, 219–227. doi: 10.1007/s001270170052
Diamond, A. (2005) Attention-deficit disorder (attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder without hyperactivity): a neurobiologically and behaviorally distinct disorder from ADHD attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (with hyperactivity). Development & Psychopathology, 17, 807–825. doi: 10.1017/ S0954579405050388
Feingold, D., Weiser, M., & Rehm, J. et al. (2016) The association between cannabis use and anxiety disorders: results from a population based representative sample. EurNeuropsychopharmacol, 26, 493–505. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2015.12.037
Feingold, D., Weiser, M., & Rehm, J. et al. (2015) The association between cannabis use and mood disorders: a longitudinal study. J Affect Disord, 172, 211–218. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2014.10.006
Fisoun,V., Floros,G., & Siomos, K. et al. (2012) Internet addiction as an important predictor in early detection of adolescent drug use experience-implications for research and practice. Journal of Addiction Medicine, 6(1), 77–84. doi: 10.1097/ADM.0b013e318233d637
Greenfield, D. N. (2018) Treatment Considerations in Internet and Video Game Addiction: A Qualitative Discussion. Child and adolescent psychiatric clinics of North America. doi: 10.1016/j.chc.2017.11.007
Ha, J.H., Yoo, H.J., Cho, I.H., Chin, B., Shin, D., & Kim, J.H. (2006) Psychiatry comorbidity assessed in Korean children and adolescents who screen positive for Internet addiction. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, .67, 821–826. doi: 10.4088/JCP.v67n0517
Kedzior, K.K., & Laeber, L.T. (2014) A positive association between anxiety disorders and cannabis use or cannabis use disorders in the general population a meta analysis of 31 studies. BMC Psychiatry, 14(1), 1–39. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-14-136
Korkeila, J., KaarlasS., & Jaaskelainen, M. et al. (2009) Attached to the web – harmful use of the Internet and its correlates. European Psychiatry, 25, 236–241. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2009.02.008
Malygin, V.L., Merkuryeva, Yu.A., & Krasnov, I.O. (2015) Neuropsychological features as risk factors of Internet-dependent behaviour in adolescents. [Meditsinskaya psikhologiya v Rossii]. 4(33), 12. Retrieved from: http://www.medpsy.ru/mprj/archiv_global/2015_4_33/nomer04.php (accessed July 12, 2018).
Malygin, V.L., Khomeriki, N.S., & Antonenko, A.A. (2015) Individual psychological properties of adolescents as risk factors of Internet-dependent behaviour. [Meditsinskaya psikhologiya v Rossii], 1(30), 7. Retrieved from: http://www.medpsy.ru/mprj/archiv_global/2015_1_30/nomer10.php (accessed July 12, 2018).
Mendelevich, V.D. (ed.) (2007) Guide to addictology. St. Petersburg, Rech’.
Nathan, D., Shukla, L., Kandasamy, A., Benegal, V. (2016) J. Behav Addict. 2016 May, 9, 1–5.
Nie, J., Zhang, W., Chen, J., & Li, W. (2016) Impaired inhibition and working memory in response to internet-related words among adolescents with internet addiction: A comparison with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Psychiatry Res. 2016 Feb,28, 236, 28–34. doi: 10.1016/j. psychres.2016.01.004
Rabadanova, A.I. et al. (2017) Electrical brain activity and interhemispheric interactions while developing Internet addiction. [Izvestiya Samarskogo nauchnogo tsentra Rossiyskoy akademii nauk], 19(2–3), 518–522.
Sanders, J., & Williams, R. (2018) The Relationship Between Video Gaming, Gambling, and Problematic Levels of Video Gaming and Gambling. Journal of gambling studies, 1–11. doi: 10.1007/s10899-018-9798-3
Sepede, G., Tavino, M., Santacroce, R., Fiori, F., Salerno, R.M., & Di Giannantonio, M. (2016) Functional magnetic resonance imaging of internet addiction in young adults. World J Radiol. 2016 Feb 28, 8(2), 210–225. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v8.i2.210. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v8.i2.210
Sinevich, A.A., & Kopytova, A.V. (2015) Analysis of motives for consuming smoking mixtures in males from the Republic of Belarus. [16y S’ezd psikhiatrov Rossii. Vserossiyskaya nauchno-prakticheskaya konferentsiya s mezhdunarodnym uchastiem «Psikhiatriya na etapakh reform: problemy i perspektivy»]. Kazan, September 23-26, 2015, abstracts of the reports. Kazan, 428–429.
Tateno, M. et al. (2018) Internet Addiction and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder Traits among Female College Students in Japan. Journal of the Korean Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry., 29(3), 144–148.
Tkachenko, G.A., & Yakovlev, V.A. (2015) Influence of emotional intelligence on the dependence on psychoactive substances. [Zhurnal gumanitarnykh nauk], 11, 110–112.
Toftdahl, N.G., Nordentoft, M., & Hjorthj, C. (2016) Prevalence of substance use disorders in psychiatric patients: a nationwide Danish population based study. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol, 51, 129–140.
Weinstein, A. (2015) Internet addiction: diagnosis, comorbidity and treatment. [Meditsinskaya psikhologiya v Rossii], 4(33), 3. Retrieved from: URL: http://mprj.ru/archiv_global/2015_4_33/nomer05.php – (accessed July 12, 2018).
Yakovlev, A.N. et al. The risk of drug use in adolescents with problem behaviour: analysis of genetic factors and the «search for novelty». [16y S’ezd psikhiatrov Rossii. Vserossiyskaya nauchno-prakticheskaya konferentsiya s mezhdunarodnym uchastiem «Psikhiatriya na etapakh reform: problemy i perspektivy»]. Kazan, September 23–26, 2015, abstracts of the reports. Kazan, 446.
Yen, J.Y., Ko, C.H., Yen, C.F. & et al. (2009) The association between harmful alcohol use and Internet addiction among college students: comparison of personality. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 63(2), 218.
For citing this article:
Malygin V.L., Merkurieva Yu.A., Shevchenko Yu.S., Malygin Ya.V., Ponomareva M.V. (2018) Psychological features and social adaptation of internet-addicted adolescents and adolescents with cannabinoid addiction. National Psychological Journal. 3, 90-97.


