Research of psycho-emotional stability in the basal emotions matrix
Recieved: 09/16/2016
Accepted: 10/20/2016
Published: 12/30/2016
Pages: 98-107
DOI: 10.11621/npj.2016.0412
Keywords: the basal emotions matrix; the tension of the psycho-emotional state; mimic pattern; epilepsy; psycho-emotional balance; psychological stability; rigidity
Available online: 30.12.2016
Volov, Vyacheslav T., Volov, Vsevolod V. (2016). Research of psycho-emotional stability in the basal emotions matrix. National Psychological Journal, (2) , 98-107. https://doi.org/10.11621/npj.2016.0412
Copied to Clipboard
CopyAbstract
The paper presents the analysis of psycho-emotional state estimation, which is based on the facial feedback monitoring. The myographic research data revealed qualitative and quantitative singularities of epileptics on the range of basal emotion indicators which have been received on the matrix method way basis and model of quality diagnostics.
For the calibration method the study involved healthy subjects. Beforehand myographic cards were developed to measure the tone of facial muscles during the trial of six basal emotions. The experiment was arranged in such a way as to reflect the work of reverse afferentation emotions. Ahe amplitude-frequency characteristics of the samples and emotional reactions of involuntary reactions were identical. Therefore samples of complementary development of natural emotions were tried: the first test stage included efferent synthesis, the second stage used afferent synthesis.
Defining features of emotional response was carried out on the basis of the model of quality diagnostics of emotions. The chiral effects were identified: mimic pattern emotions in both samples. This effect allowed to separate violations of the personal response from the specific pattern, which blocks the effects of restrictions and other emotions. The matrix method allowed to produce quantitative estimates of mental and emotional state on the basis of instrumental measurements of basal emotions. In the group of epileptics, on the facial expression level emotional blocks are identified which are connected with ceral effects (repented characteristic deviation of emotional patterns in the two probes).
Additionally differences on quantitative estimations between the epileptics reactions and healthy individuals are revealed.
Table 1. The orthogonal matrix of basic emotions (MBE)
|
Emotions |
X1 (Anger) |
X2 (Joy) |
X3 (Surprise) |
|
Y1 (Fear) |
Z11 |
Z12 |
Z13 |
|
Y2 (Sorrow) |
Z21 |
Z22 |
Z23 |
|
Y3 (Disgust) |
Z31 |
Z32 |
Z33 |
Table 2. Energy Indicators of MBE
|
Indicators EMG* (Healthy) |
Indicators EMG (Healthy) |
Differences, % |
||
|
L |
ε |
L |
ε |
ε |
|
47 |
0.18 |
86 |
0.245 |
26.5% |
|
Indicators EMG (Sick) |
Indicators EMG (Sick) |
Differences, % |
||
|
L |
ε |
L |
ε |
ε |
|
46 |
0.18 |
86 |
0.31 |
42% |
Table 3. Energy indicators in different clinical groups
|
Energy indicators in different clinical groups |
Rare Generalized Seizures (Group 1) |
Frequent Generalized Seizures (Group 2) |
Partial Equivalents (Group 3) |
Remission (Group 4) |
|
(ε) |
0.18 |
0.23 |
0.22 |
0.17 |
|
(L) |
49.6 |
85.86 |
61.77 |
77.71 |
|
(εL) |
9.59 |
20.5 |
14.6 |
14.4 |
|
H |
0.613 |
0.66 |
0.64 |
0.64 |
|
I |
0.67 |
0.45 |
0.73 |
0.71 |
Table 4. Energy indicators of groups with chiral effects
|
Energy indicators |
Pair 1 |
Pair 2 |
Pair 3 |
|||
|
(1-1) |
(1-2) |
(2-1) |
(2-2) |
(3-1) |
(3-2) |
|
|
ε |
0.21 |
0.22 |
0.189 |
0.197 |
0.228 |
0.187 |
|
L |
65.92 |
60.04 |
51.23 |
60.28 |
50.29 |
63.5 |
|
εL |
14.30 |
14.93 |
10.004 |
12.857 |
12.37 |
12.727 |
|
H |
0.646 |
0.638 |
0.624 |
0.632 |
0.639 |
0.63 |
|
I |
0.606 |
0.638 |
0.673 |
0.665 |
0.603 |
0.681 |
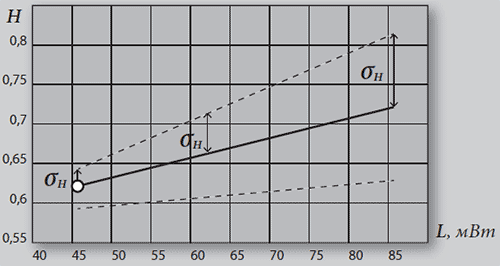
Figure 1. Dependence of the entropy on the MBE tension in the healthy group, σH is the meansquare deviation of mentally healthy patients
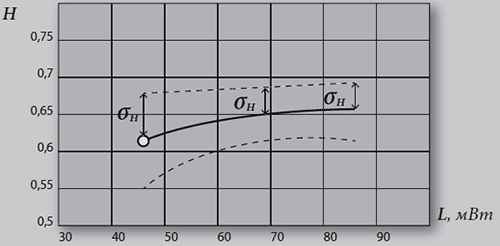
Figure 2. Dependence of the entropy on the MBE tension in the epilepsy group, σH is the meansquare deviation of sick patients
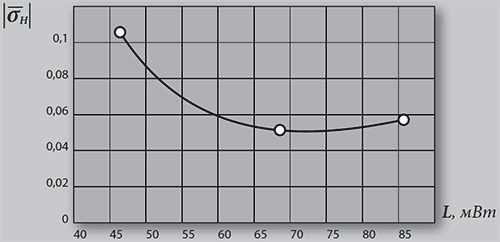
Figure 3. Entropy volatility rate in the group of epilepsy patients
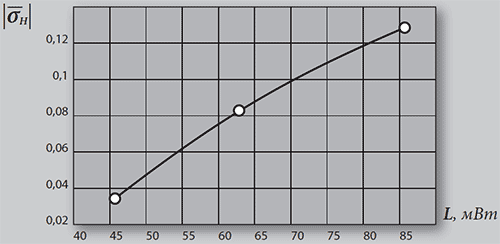
Figure 4. Entropy volatility rate in the group of mentally healthy patients
References:
Anokhin, P.K. (1980) Nodal questions of functional systems theory. Moscow, Nauka, 197.
Bekhtereva, N.P. (2013) The magic of the brain. Moscow, Astrel, 384.
Boldyrev, A.I. (2000) Mental characteristics of patients with epilepsy. Moscow, Meditsina, 370.
Gantmakher, F.R. (2010) The theory of matrices. Moscow, FIZMATLIT, 558. ISBN 978-5-9221-0524-8
Izard, K.E. (2012) Psychology of emotions. St. Petersburg, Piter, 464. ISBN 978-5-314-00067-0
Ilyin, S.P. (2012) Psychology of emotions. St. Petersburg, Piter, 783.
Khomskaya, E.D. (1992) The brain and emotion. Moscow, 192.
Lebedinskiy, V., Nicholas, O., & Baenskaya E.R. et al. (1990) Emotional disorders in childhood. Moscow, Izdatel’stvo Moskovskogo Universiteta, 198.
Luria, A.R. (2007) Lectures on general psychology. St. Petersburg, Piter, 112.
Lyapunov, A.M. (1950) The general issues of motion stability. Moscow, Gosudarstvennoe Izdatel’stvo tehnichesko-theoreticheskoy literatury, 472.
Martin, H., & England, J. (1988) The mathematical theory of entropy. Moscow, Mir, 354.
Meltyff, A.N., & Gopnik, A. (1993) The role of imitation in understanding persons and developing a theory of mind. Understanding other minds: perspectives from autism. Oxford.
Prigogine, I. (1973) Thermodynamic Theory of Structure. Moscow, Mir, 280.
Rusalova, M.N. (1979) Experimental studies. Moscow, 179.
Simonov, P.V. (2004) Selected works. In 2 vols. Vol. 1. [Mozg: emotsii, potrebnosti, potrebnosti, povedenie]. Moscow, Nauka, 438. ISBN 5-02-033053-1
Volov, V.T., & Volov, V.V. Investigation of functional systems of the psychic self-organization based on the method of basal matrix. Cornell university library. Neurons and Cognition (q-bio.NC) Cite as: arXiv:1510.02679 [q-bio.NC] (Submitted on 9 Oct 2015).
Volov, V.V. (2008) Methodology for functional systems of psychic self. [Izvestiya samarskogo nauchnogo tsentra RAN. Spetsial'nyy vypusk. Aktual'nye problemy psikhologii]. Samara, 44-48
Volov, V.V. (2015) Features of emotional response system in a paroxysmal brain. [Sibirskiy psikhologicheskiy zhurnal]. 56, 122-137. doi: 10.17223/17267080/56/10
Zalevskiy, G.V. (1993) Mental rigidity in health and disease. Tomsk, Izdatel’stvo Tomskogo Universiteta, 271. ISBN 5-7511-0593-1
Zalevskiy, G.V., & Rogovin, M.S. (1970) Fixed forms of behaviour and their implications for neurological and psychiatric clinics. Report 2. Rigidity. [Zhurnal Neyropatologii i Psikhiatrii im. S.S. Korsakova]. Vol. LXX. Vol. 9, 1404-1417.Volov, Vyacheslav T., Volov, Vsevolod V.. Research of psycho-emotional stability in the basal emotions matrix. // National Psychological Journal 2016. 2. Pages98-107. doi: 10.11621/npj.2016.0412
Copied to Clipboard
Copy

